This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Band structure of nanocrystals
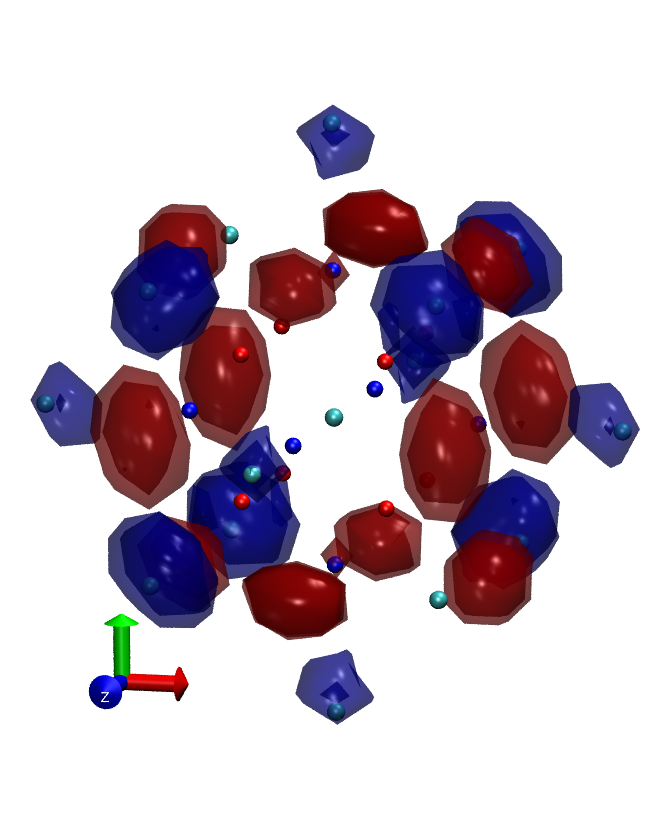
The 'fuzzy band structure' of an nanocrystal (i.e. cluster without periodic boundary condition) can be obtained by Fourier transform of it's eigenstates. See Hapala et.al,Phys.Rev.B87,195420. In fireball there are two methods to do this projection.
- 3D Fourier transform of molecular orbitals - in this method we choose several molecular orbitals, project them on grid and let fireball execute Fast fourier transform on this grid. The problem is that the result is complex ( real part correspond to symmetric components of the real wavefunction and imaginary part to antisymetric componenets ). For easier visualization we compute square of absolute value, which corresponds to density of the state in k-space. This property is exported as .xsf file.
- projection of Molecular orbitals on planewaves sampled along some 1D lines in k-space - again, molecular orbitals are first projected onto real space grid, then on this gird are multiplied by planewave and product is integrated.
Availability
this is implemented only in Prokop's personal versions of Fireball located in
/data/home/hapala/Fireball_dev/src_1.0-BSfinal /data/home/hapala/Fireball_dev/progs_Jellium_mod
3D Fourier fransform of Molecular Orbitals
Interface for outputing 3D fourier transform of MOs is modified form standard interface for outputting real-space projection of MOs. You have to switch on iwrtewf = 1 and set iewform = 5. Than you choose particular set of MO to plot by npbands and pbands. The example fireball.in looks like this:
fireball.in
&OPTION basisfile = answer.bas nstepf = 1 icluster = 1 ifixcharge = 1 dt = 0.5 &END &OUTPUT iwrtewf = 1 &END &MESH iewform = 5 npbands = 5 pbands = 159,160,161,162,163 &END
You have to provide also file called kmap.optional where are written more speccific stettings. In this file you can choose byEnerg option to automatically evaluate all orbitals in particular energy windows Emin and Emax instead of listing all orbitals in pbands variable. Then there are options of different output format - either 3D grid in .xsf or 2D image .ppn. Both options can be switched on simultaneously. In case you choose the .ppn image the 3D grid is collapsed into 2D by evaluationg maximum along z-axis. You can also plot independently real and imaginary part of projection ( instead of just square of absolute value) by option PlotImag .
Then there are some very specific options GetMaxPos to output position of global maximum projection for each orbital, and ValIn to output value of the projection in particular set of points in k-space. This options are here mostly for historical reasons, and I don't expect they will be much used in general. They are shortly describet later, for completness.
The example of kmap.optional looks like:
1 # byEnerg - if 1 choose orbitals by energy range else choose by pbands list -8.59705 1.09186 # Emin Emax - energy range 0 # PlotXSF? - save .xsf files 0 # PlotPPN? - save 2D projectins (max along z-axis) into ppn image file for quick overview 0 # PlotImag? - save real and imaginery part to independent files fft_Im_XXXX.xsf and fft_Re_XXXX.xsf 1 # GetMaxPos - if 1 for each MO writes out position of global maximum of k-space density int kmaxs.dat 5.50 # alat - lattice constant in angstroem 0 # ValIn - write out value in different points defined in ksamples.optional
If you choose ValIn option you have to specify points in k-space where the value of projection should be taken. This is done in ksample.optional file. Example of ksample.optional file is there:
ksample.optional
26 nksamples 2.0 0.0 0.0 # HOMOs Gamma 100 0.0 2.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 2.0 -2.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 -2.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 -2.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 # HOMOs Gamma 111 -1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 -1.0 1.0 -1.0 -1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 -1.0 -1.0 1.0 -1.0 1.0 -1.0 -1.0 -1.0 -1.0 -1.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 # LUMOs X 0.0 -1.0 1.0 0.0 1.0 -1.0 0.0 -1.0 -1.0 1.0 0.0 1.0 -1.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 -1.0 -1.0 0.0 -1.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 -1.0 1.0 0.0 1.0 -1.0 0.0 -1.0 -1.0 0.0
Output
The code outputs fourier_XXXX.xsf if you choose writeXSF and orbfft_XXXX.ppm if you choose writePPN option.
If you choose PlotImag option you in adition get separate real and imaginary part of projection ( corresponds to symmetric and antisymmetric component ) in files fft_Im_XXXX.xsf and fft_Re_XXXX.xsf.
If you choose option GetMaxPos you obtaion file kmaxs.dat with following structure:
kmaxs.dat
iband, Ei imax, jmax, kmax, ValMax, rimax, rjmax, rkmax 107 -7.40951516 -3 -3 -3 2968.71621697 -0.70854607 -0.70769619 -0.70733483 108 -7.38731466 -4 -3 -2 3133.46757266 -0.94472810 -0.70769619 -0.47155655 109 -7.38677828 -4 -2 -3 3128.34104148 -0.94472810 -0.47179746 -0.70733483 110 -7.26838823 -4 -4 0 1878.06049291 -0.94472810 -0.94359492 0.00000000 ...
where Ei is eigenvalue of the MO, (imax,jmax,kmax) is index of position of maximum inside the grid, ValMax is value of projection in the maximum, and (rimax,rjmax,rkmax) are coordinates of the maximum in multiples of reciprocal lattice vector.
ksamples.dat
Ei rho(k1) rho(k2) rho(k3) rho(k4) rho(k5) rho(k6) -2.08815 16.68657904 3.16266264 10.09450414 16.68657904 3.16266264 10.09450414 ... -2.08681 5.87885299 17.02497532 10.22090870 5.87885299 17.02497532 10.22090870 ... -2.06449 28.89941918 27.76432636 29.01794378 28.89941918 27.76432636 29.01794378 ... ...
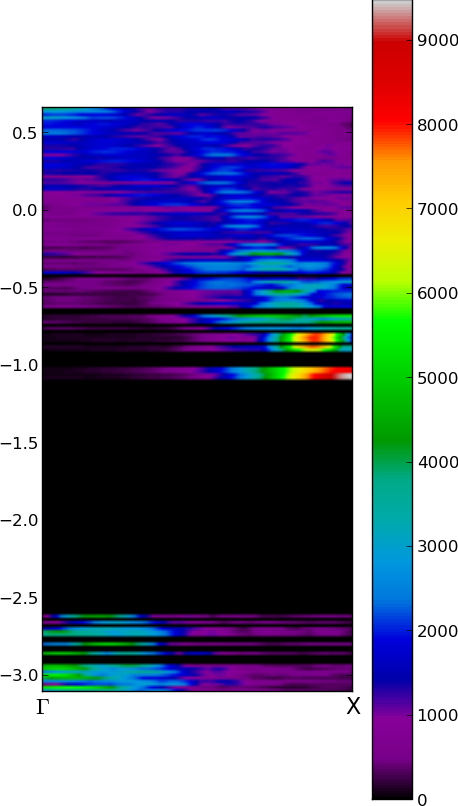
1D cuts of Fuzzy Band Structure
fireball.in
&OPTION basisfile = answer.bas nstepf = 1 icluster = 1 ifixcharge = 1 dt = 0.5 &END &OUTPUT iwrtewf = 1 &END &MESH iewform = 6 &END
kscan.optional
1 # byEnerg -8.0000 1.0000 # Emin Emax 5.50 # alat 48 100 # nlines nkpoints 2.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 2.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 -1.0 0.0 2.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 1.0 2.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 -1.0 0.0 2.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 2.0 0.0 -1.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 2.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 2.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 -1.0 0.0 0.0 2.0 -1.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 2.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 2.0 0.0 -1.0 1.0 -2.0 0.0 0.0 -1.0 1.0 0.0 -2.0 0.0 0.0 -1.0 -1.0 0.0 -2.0 0.0 0.0 -1.0 0.0 1.0 -2.0 0.0 0.0 -1.0 0.0 -1.0 0.0 -2.0 0.0 1.0 -1.0 0.0 0.0 -2.0 0.0 -1.0 -1.0 0.0 0.0 -2.0 0.0 0.0 -1.0 1.0 0.0 -2.0 0.0 0.0 -1.0 -1.0 0.0 0.0 -2.0 1.0 0.0 -1.0 0.0 0.0 -2.0 -1.0 0.0 -1.0 0.0 0.0 -2.0 0.0 1.0 -1.0 0.0 0.0 -2.0 0.0 -1.0 -1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 -1.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 -1.0 1.0 1.0 -1.0 0.0 1.0 -1.0 1.0 1.0 -1.0 1.0 0.0 1.0 -1.0 1.0 0.0 -1.0 1.0 1.0 -1.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 -1.0 1.0 1.0 -1.0 0.0 -1.0 -1.0 1.0 0.0 -1.0 1.0 -1.0 -1.0 1.0 -1.0 0.0 1.0 -1.0 -1.0 1.0 -1.0 -1.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 -1.0 0.0 1.0 -1.0 1.0 1.0 -1.0 1.0 0.0 -1.0 1.0 1.0 -1.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 -1.0 1.0 -1.0 0.0 1.0 -1.0 -1.0 1.0 -1.0 -1.0 0.0 -1.0 -1.0 1.0 -1.0 -1.0 1.0 0.0 1.0 -1.0 -1.0 0.0 -1.0 -1.0 1.0 -1.0 -1.0 1.0 0.0 -1.0 1.0 -1.0 -1.0 1.0 -1.0 0.0 -1.0 -1.0 -1.0 0.0 -1.0 -1.0 -1.0 -1.0 -1.0 -1.0 0.0 -1.0 -1.0 -1.0 -1.0 -1.0 -1.0 0.0
klines_XXXXX.dat
1 391.30476603 391.30476603 391.30476603 391.30476603 287.45162513 ...
2 391.20959758 391.21921233 390.08793464 391.61800721 295.99428664 ...
3 389.17880205 389.77130848 387.81208053 388.10778349 306.53352273 ...
...
klines_TOT.dat
Ei rho(k1) rho(k2) rho(k3) rho(k4) rho(k5) ... -7.99755 413.91048549 428.76133304 440.87314746 450.14882297 456.52837031 ... -7.99140 394.18797633 403.02567283 409.86012222 414.38007661 416.29758353 ... -7.97472 418.51477832 433.83793597 448.50901654 462.18377663 474.53904963 ... -7.96729 262.72449682 269.69434762 274.26597685 275.89514172 285.23659456 ... ...
plotting results
#!/usr/bin/python
from pylab import *
import numpy
dE = 0.02 # [ eV ]choose width of energy-bins for plotting
F = transpose(genfromtxt( 'klines_TOT.dat' ))
Es = F[0]
Ps = transpose(F[1:])
Emin =Es.min(); Emax =Es.max()
Pgrid = zeros( ( int( (Emax-Emin)/dE )+1 , shape(Ps)[1] ) )
n = len(Es)
for i in range(n):
iE = int((Es[i]-Emin)/dE)
#Pgrid[iE] += Ps[i] # overlaping (=degenerated) states are summed up
Pgrid[iE] = numpy.vstack([Pgrid[iE],Ps[i] ]).max(axis=0) # for overlaping (=degenerated) states is taken maximum
# choose color map reference here http://wiki.scipy.org/Cookbook/Matplotlib/Show_colormaps
cmap='spectral'
figure( figsize=(5,10) )
extent = ( 0,2, Emin, Emax )
imshow( Pgrid, origin='image', extent=extent, cmap = cmap )
xticks([0,2] , ['$\Gamma$','X'], fontsize=16) # x-axis ticks Gamma and X vector
colorbar()
savefig('FuzzyBand.png', bbox_inches='tight' )
show()